The WrightCurriculum began in 2017 with the entering class of 2021 after years of planning, prioritizing content, and field-testing teaching and learning strategies. The three most important principles for the design of the WrightCurriculum are the following:
- Students will become self-directed learners with specific skills in critical thinking, discovering best evidence to make decisions, and how to keep learning throughout a life of service in the practice of medicine
- The design, structure, and strategies for teaching and learning are evidence-based and linked to the science of learning
- The curriculum will continue to evolve as faculty and students learn together ‘what works best’ within a learning environment of collaboration, respect, and integrity
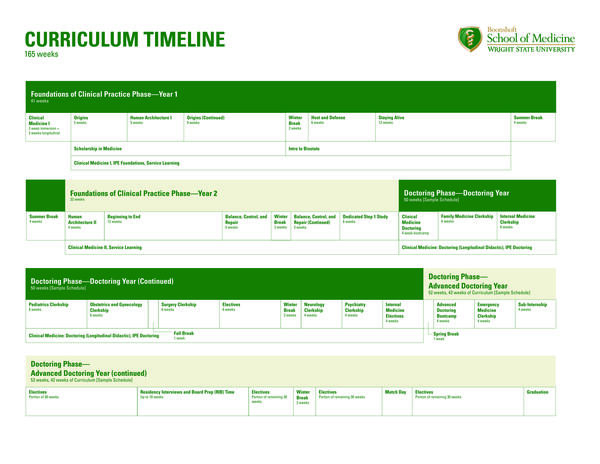
There are two phases:

