Unlike traditional curricula, this lecture-free pre-clinical curriculum integrates the learning of the “normal” and “abnormal” within the context of clinical application. Students master assigned content outside the classroom so that classroom time with faculty is devoted to applying content to answer high-order-thinking USMLE-style questions about biomedical concepts and clinical application. Teaching by the faculty becomes focused on probing for deeper understanding and clarifying misconceptions. Classroom time is interactive, with students highly engaged in their learning. The primary modalities of teaching and learning throughout all Foundations modules are Peer Instruction (PI), Team-Based Learning (TBL) and WrightQ (our version of problem-based learning). Exams given throughout a module contain an individual and a group component: students first complete the exam individually, and then in small groups. Thus, there is a formative component to assessments throughout the modules. End of module summative exams are given individually only, to ensure that students master the necessary content.
Foundations Phase: Year 1
41 Weeks
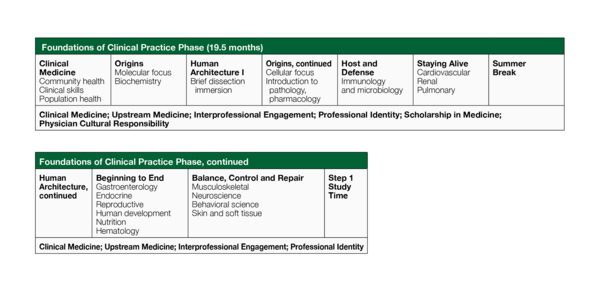
Clinical Medicine I
Longitudinal
Consists of four dimensions: 1) Clinical Skills, 2) Upstream Medicine (populations health, social determinants of health, health care policy and delivery, value based care, and community resources), 3) Professional Skills (professionalism and professional identity formation), and 4) Nutrition and Lifestyle Medicine. Begins with two weeks of Upstream Medicine, then longitudinal meeting every Friday, providing education on interviewing and physical exam skills.
Origins
14 Weeks
Integrated module consists of cell biology, biochemistry, genetics, neurophysiology, and introductions to pathophysiology, autonomics, and pharmacology
Human Architecture I
5 Weeks
Introduction to the language and concepts of human anatomy, imaging, and embryology. Students carry out a detailed dissection of the thorax, which will prepare them for the Staying Alive module.
Host and Defense
6 Weeks
Introduction to the principles of immunology, bacteriology, and virology as they apply to human disease. Engaged learning sessions all emphasize the skills necessary to diagnose and treat infectious diseases.
Staying Alive
12 Weeks
Systems-based module focusing on the relationship between cardiac, respiratory, and renal systems under normal and abnormal conditions. Along with PI and TBL, our version of problem-based learning, WrightQ is first introduced during this module.
Scholarship in Medicine
Longitudinal
Module meeting weekly for a total of 12 weeks, ensures that students engage in instruction in the scientific method and collect and/or use data to test and verify hypotheses and address questions about biomedical phenomena and how it contributes to the body of scientific knowledge to improve the health pf patients and/or populations.
Introduction to Biostatistics
Longitudinal
Self-paced module that provides an introduction to biostatistics topics.
Interprofessional Engagement
Longitudinal
During the course of the Foundations Phase, students are required to participate in interprofessional activities with other health professions
Foundations Phase: Year 2
32 Weeks
Clinical Medicine II
Longitudinal
Continues with dimensions of Clinical skills, Upstream Medicine, and Professional Skills, meets weekly on Fridays.
Human Architecture II
4 Weeks
Continue with dissection of the body, including neck, abdominal wall, and pelvis. Preparing students for the structures they will continue to learn about in Beginning to End and Balance, Control and Repair.
Beginning to End
12 Weeks
Systems-based module focusing on the endocrine, gastrointestinal, and reproductive systems under normal and abnormal conditions. This module asl advances the concepts of nutrition, hematology, and human development.
Balance, Control and Repair
10 Weeks
Systems-based module focusing on the normal structure, function, and disease of the nervous system, musculoskeletal and integumentary systems, and behavioral science.
Biostatistics II
Longitudinal
Self-paced module that provides a continuation of biostatistics topics.
Service Learning
Longitudinal
During the course of the Foundations phase, students are required to complete 16 hours of service learning, document the hours, and complete a reflection on their service learning experience and how it relates to a commitment to medicine as a life of service, among other prompts.
Step 1 Study
6 Weeks
Dedicated time for students to study and take USMLE Step 1. Students who may need more focused assistance work with faculty and learning specialists during this time to be better prepared for success.
